
-aniaostudio-
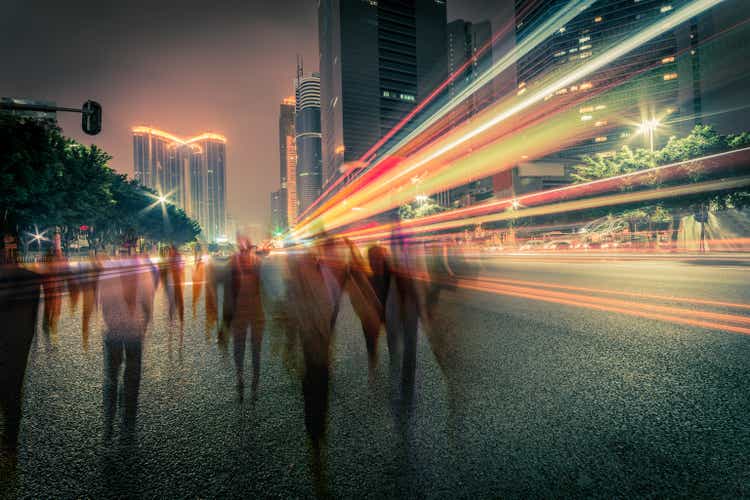
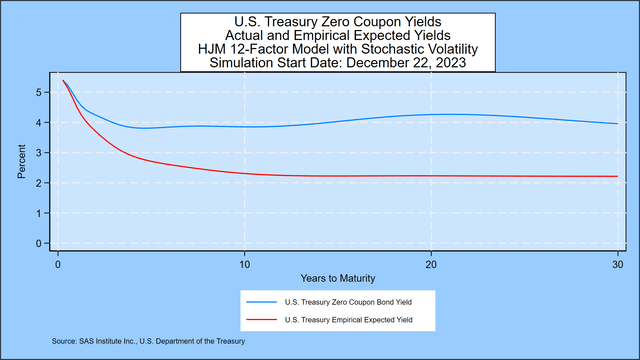
As defined in Prof. Robert Jarrow’s ebook cited under, ahead charges comprise a danger premium above and past the market’s expectations for the 3-month ahead fee. We doc the scale of that danger premium on this graph, which reveals the zero-coupon yield curve implied by present Treasury costs in contrast with the annualized compounded yield on 3-month Treasury payments that market contributors would anticipate based mostly on the every day motion of presidency bond yields in 14 international locations since 1962. The danger premium, the reward for a long-term funding, is massive and widens over many of the maturity vary to 30 years. The graph additionally reveals a pointy downward shift in yields within the first few years, then the decline continues at a gradual however regular tempo for nearly 30 years. We clarify the small print under.
SAS Institute Inc.
For extra on this subject, see the evaluation of presidency bond yields in 14 international locations by means of November 30, 2023 given within the appendix.
Inverted Yields, Damaging Charges, and U.S. Treasury Chances 10 Years Ahead
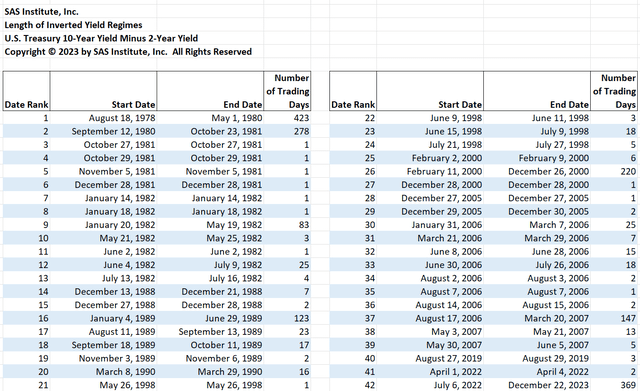
The damaging 2-year/10-year Treasury unfold has now continued for 369 buying and selling days. The unfold is at present at a damaging 41 foundation factors in comparison with damaging 53 final week. The desk under reveals that the present streak of inverted yield curves is the second longest within the U.S. Treasury market because the 2-year Treasury yield was first reported on June 1, 1976. To this point, the longest streak is 423 buying and selling days beginning on August 18, 1978, however that streak is in jeopardy.
SAS Institute Inc.
On this week’s forecast, the main target is on three parts of rate of interest habits: the longer term likelihood of the recession-predicting inverted yield curve, the likelihood of damaging charges, and the likelihood distribution of U.S. Treasury yields over the following decade.
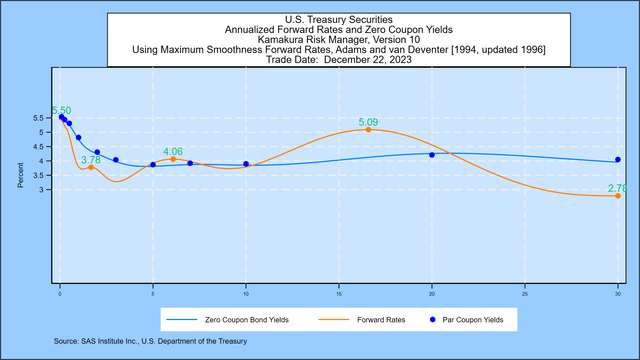
We begin from the closing U.S. Treasury yield curve printed every day by the U.S. Division of the Treasury. Utilizing a most smoothness ahead fee method, Friday’s implied ahead fee curve reveals a fast rise in 1-month ahead charges to an preliminary peak of 5.50%, versus 5.50% final week. After the preliminary rise, there’s a decline till charges peak once more at 4.06%, in comparison with 4.04% final week. Charges lastly peak once more at 5.09%, in comparison with 5.02% final week, after which they do not want to a decrease plateau on the finish of the 30-year horizon.
SAS Institute Inc.
Utilizing the methodology outlined within the appendix, we simulate 100,000 future paths for the U.S. Treasury yield curve out to thirty years. The subsequent three sections summarize our conclusions from that simulation.
Inverted Treasury Yields: Inverted Now, 66.4% Chance by June 21, 2024
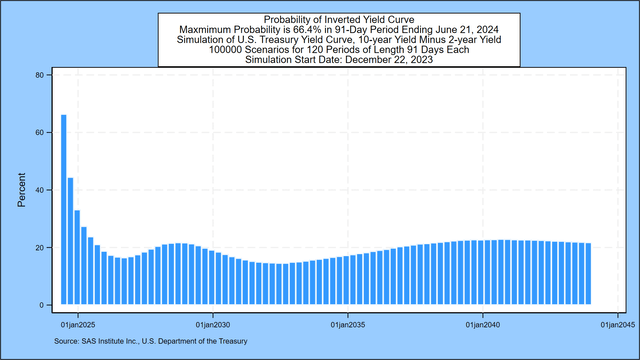
Numerous economists have concluded {that a} downward sloping U.S. Treasury yield curve is a vital indicator of future recessions. A current instance is that this paper by Alex Domash and Lawrence H. Summers. We measure the likelihood that the 10-year par coupon Treasury yield is decrease than the 2-year par coupon Treasury for each situation in every of the primary 80 quarterly intervals within the simulation.[1] The subsequent graph reveals that the likelihood of an inverted yield has dropped, peaking at 66.4%, in comparison with 76.5% one week earlier than, within the 91-day quarterly interval ending June 21, 2024.
SAS Institute Inc.
Damaging Treasury Invoice Yields: 13.3% Chance by March 11, 2033
The subsequent graph describes the likelihood of damaging 3-month Treasury invoice charges for all however the first 3 months of the following 3 a long time. The likelihood of damaging charges begins close to zero however peaks at 13.3%, in comparison with 13.4% one week earlier, within the interval ending March 11, 2033:
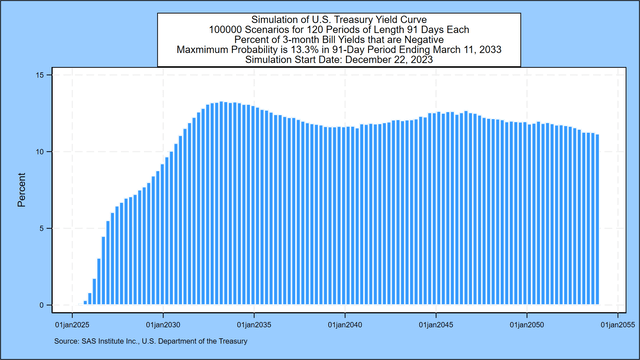
SAS Institute Inc.
Calculating the Default Threat from Curiosity Fee Maturity Mismatches
In mild of the interest-rate-risk-driven failure of Silicon Valley Financial institution on March 10, 2023, we now have added a desk that applies equally properly to banks, institutional investor, and particular person investor mismatches from shopping for long-term Treasury bonds with borrowed short-term funds. We assume that the only real asset is a 10-year Treasury bond bought at time zero at par worth of $100. We analyze default danger for 4 completely different preliminary market worth of fairness to market worth of asset ratios: 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20%. For the banking instance, we assume that the one class of liabilities is deposits that may be withdrawn at par at any time. Within the institutional and retail investor case, we assume that the legal responsibility is basically a borrowing on margin/repurchase settlement with the opportunity of margin calls. For all traders, the quantity of liabilities (95, 90, 85 or 80) represents a “strike value” on a put choice held by the legal responsibility holders. Failure happens through a margin name, financial institution run, or regulatory take-over (within the banking case) when the worth of belongings falls under the worth of liabilities.
The graph under reveals the cumulative 10-year possibilities of failure for every of the 4 potential capital ratios when the asset’s maturity is 10 years. For the 5 p.c case, that default likelihood is 41.27%, in comparison with 40.90% from final week.
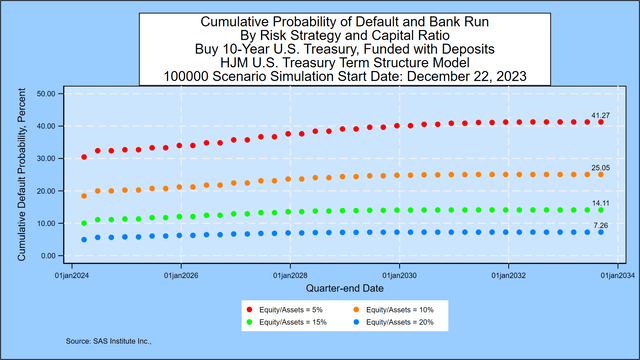
SAS Institute Inc.
This default likelihood evaluation is up to date weekly based mostly on the U.S. Treasury yield simulation described within the subsequent part. The calculation course of is identical for any portfolio of belongings with credit score danger included.
U.S. Treasury Chances 10 Years Ahead
On this part, the main target turns to the last decade forward. This week’s simulation reveals that the almost definitely vary for the 3-month U.S. Treasury invoice yield in ten years is from 0% to 1%, unchanged from final week. There’s a 28.02% likelihood that the 3-month yield falls on this vary, a change from 28.16% one week earlier than. For the 10-year Treasury yield, the almost definitely vary is from 2% to three%, additionally unchanged from final week. The likelihood of being on this vary is 22.82%, in comparison with 23.00% one week prior.
In a current publish on Searching for Alpha, we identified {that a} forecast of “heads” or “tails” in a coin flip leaves out vital data. What a classy bettor must know is that, on common for a good coin, the likelihood of heads is 50%. A forecast that the following coin flip will likely be “heads” is actually value nothing to traders as a result of the result is solely random.
The identical is true for rates of interest.
On this part we current the detailed likelihood distribution for each the 3-month Treasury invoice fee and the 10-year U.S. Treasury yield 10 years ahead utilizing semi-annual time steps.[2] We current the likelihood of the place charges will likely be at every time step in 1 p.c “fee buckets.” The forecast for 3-month Treasury yields is proven on this graph:
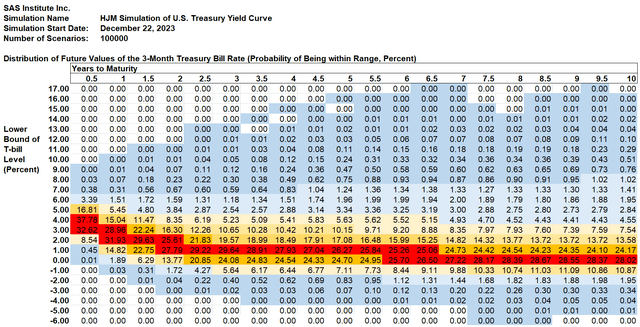
SAS Institute Inc.
3-Month U.S. Treasury Yield Information:
The likelihood that the 3-month Treasury invoice yield will likely be between 1% and a couple of% in 2 years is proven in column 4: 27.79%. The likelihood that the 3-month Treasury invoice yield will likely be damaging (because it has been typically in Europe and Japan) in 2 years is 1.72% plus 0.04% plus 0.00% = 1.76% (distinction on account of rounding). Cells shaded in blue signify optimistic possibilities of occurring, however the likelihood has been rounded to the closest 0.01%. The shading scheme works like this:
- Darkish blue: the likelihood is bigger than 0% however lower than 1%
- Mild blue: the likelihood is bigger than or equal to 1% and fewer than 5%
- Mild yellow: the likelihood is bigger than or equal to five% and 10%
- Medium yellow: the likelihood is bigger than or equal to 10% and fewer than 20%
- Orange: the likelihood is bigger than or equal to twenty% and fewer than 25%
- Pink: the likelihood is bigger than 25%
The chart under reveals the identical possibilities for the 10-year U.S. Treasury yield derived as a part of the identical simulation.
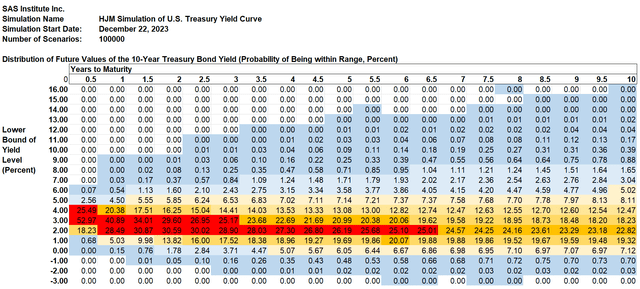
SAS Institute Inc.
10-Yr US Treasury Yield Information:
Appendix: Treasury Simulation Methodology
The possibilities are derived utilizing the identical methodology that SAS Institute Inc. recommends to its KRIS® and Kamakura Threat Supervisor® shoppers. A reasonably technical rationalization is given later within the appendix, however we summarize it in plain English first.
Step 1: We take the closing U.S. Treasury yield curve as our start line.
Step 2: We use the variety of factors on the yield curve that greatest explains historic yield curve shifts. Utilizing every day authorities bond yield knowledge from 14 international locations from 1962 by means of November 30, 2023, we conclude that 12 “components” drive virtually all actions of presidency bond yields. The international locations on which the evaluation is predicated are Australia, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, New Zealand. Russia, Singapore, Spain, Sweden, Thailand, the UK, and the USA of America. No knowledge from Russia is included after January, 2022.
Step 3: We measure the volatility of adjustments in these components and the way volatility has modified over the identical interval.
Step 4: Utilizing these measured volatilities, we generate 100,000 random shocks at every time step and derive the ensuing yield curve.
Step 5: We “validate” the mannequin to be sure that the simulation EXACTLY costs the beginning Treasury curve and that it matches historical past in addition to potential. The methodology for doing that is described under.
Step 6: We take all 100,000 simulated yield curves and calculate the chances that yields fall in every of the 1% “buckets” displayed within the graph.
Do Treasury Yields Precisely Replicate Anticipated Future Inflation?
We confirmed in a current publish on Searching for Alpha that, on common, traders have virtually all the time performed higher by shopping for long run bonds than by rolling over brief time period Treasury payments. That signifies that market contributors have typically (however not all the time) been correct in forecasting future inflation and including a danger premium to that forecast.
The distribution above helps traders estimate the likelihood of success from going lengthy.
Lastly, as talked about weekly within the Company Bond Investor Friday overview, the longer term bills (each the quantity and the timing) that every one traders try to cowl with their investments are an vital a part of funding technique. The creator follows his personal recommendation: cowl the short-term money wants first after which step out to cowl extra distant money wants as financial savings and funding returns accumulate.
Technical Particulars
Day by day authorities bond yields from the 14 international locations listed above type the bottom historic knowledge for becoming the variety of yield curve components and their volatility. The U.S. historic knowledge is offered by the U.S. Division of the Treasury. The usage of the worldwide bond knowledge will increase the variety of observations to greater than 105,000 and offers a extra full vary of expertise with each excessive charges and damaging charges than a U.S. knowledge set alone offers.
The modeling course of was printed in a vital paper by David Heath, Robert Jarrow and Andrew Morton in 1992:

Econometrica
For technically inclined readers, we advocate Prof. Jarrow’s ebook Modeling Mounted Earnings Securities and Curiosity Fee Choices for many who need to know precisely how the “HJM” mannequin development works.
The variety of components, 12 for the 14-country mannequin, has been secure for a while.
Footnotes:
[1] After the primary 20 years within the simulation, the 10-year Treasury can’t be derived from the preliminary 30 years of Treasury yields.
[2] The total simulation makes use of 91-day time steps for 30 years ahead. This word summarizes simply the primary 10 years of the complete simulation.




