JariJ/iStock by way of Getty Photographs
In 2023, the worldwide economic system defied widespread expectations of a recession and falling rates of interest. As an alternative, the US, Japan, and, to a lesser extent, Europe delivered considerably higher progress than was anticipated on the flip of the 12 months, even because the U.S. Federal Reserve (Fed) and the European Central Financial institution (ECB) continued to lift coverage charges by a lot of the 12 months.
Underappreciated financial progress is highly effective gasoline for international equities: the efficiency of the U.S. “Magnificent 7” shares (Apple (AAPL), Microsoft (MSFT), Alphabet (GOOG) (GOOGL), Amazon (AMZN), Nvidia (NVDA), Meta (META), and Tesla (TSLA)) is broadly mentioned, however as of December 31, 2023, German, Spanish, and Italian bourses[1] additionally returned 24.5%, 32.5%, and 39%, respectively, in U.S. greenback phrases.
That is consistent with or higher than 26.4% for the S&P 500 Index. Even Japanese equities[2] are up at double-digit charges in U.S. greenback phrases, regardless of the Japanese yen depreciating to lows final noticed within the early Nineties.
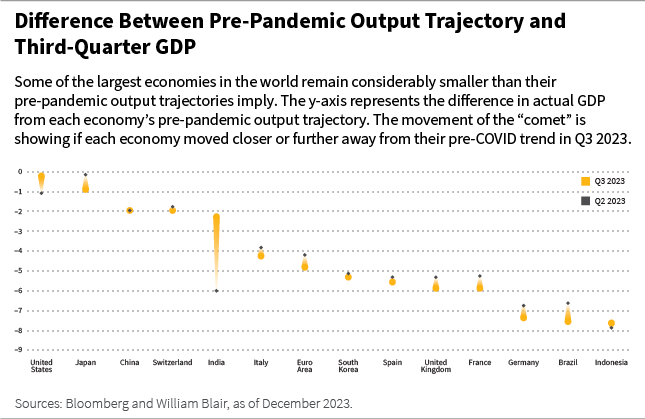
To make sure, the world economic system has some floor to cowl. On the finish of 2023, most of the largest economies stay considerably smaller than their pre-COVID progress trajectory implies, as proven within the chart beneath.
The USA and Japan are the closest, whereas the UK, Germany, and Indonesia are among the many furthest away from their pre-pandemic output trajectory.
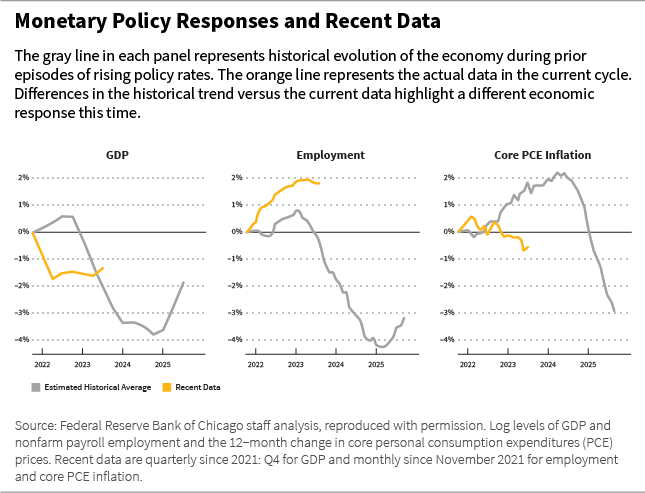
The expertise in 2023 has defied the commonplace view of an inevitable trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
Many proceed to argue that for inflation to say no to the two% vary, the economic system must shrink and unemployment must rise. This view assumes that the run-up in inflation over the past two years is due primarily to extreme demand progress.
Within the chart beneath, evaluation by the Federal Reserve Financial institution of Chicago exhibits simply how in a different way U.S. financial variables are behaving within the aftermath of the Fed’s tightening coverage and makes a strong argument that inflation this time was primarily attributable to pandemic-induced provide constraints.
Seen on this gentle, it’s hardly shocking that each the US and Europe have defied dire predictions of an imminent recession to this point.
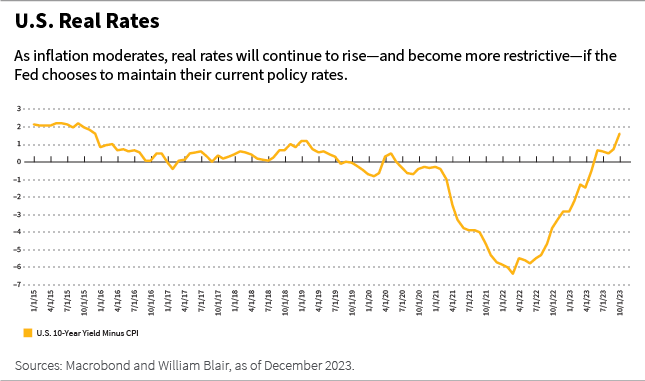
The Fed’s financial coverage stance is turning into de facto extra restrictive, as steady coverage charges amid quickly falling inflation indicate rising actual charges.
Our outlook for 2024 hinges on whether or not the Fed and the ECB can start to decrease coverage charges early sufficient to stop excessive correct charges from meaningfully dampening financial exercise.
As annual worth inflation converges again to a 2% price within the early months of 2024, present financial coverage, as measured by actual rates of interest, will grow to be de facto extra restrictive, as proven within the chart beneath.
The actual rate of interest is nothing greater than nominal charges minus inflation. Thus, decrease inflation robotically means increased actual charges if the Fed chooses to keep up present settings.
Due to this fact, we count on the Fed to start to decrease the nominal coverage price as early as the primary half of 2024, whilst home financial progress stays resilient.
The disinflation course of in the US and Europe is already nicely superior. Firstly of 2023, client costs rose by 6% year-over-year.
By the tip of the 12 months, the Shopper Value Index (CPI) registered year-on-year will increase of three.2%.
Nonetheless, the Fed’s most well-liked gauge of home inflation – PCE excluding meals and vitality, which are usually unstable – continues to be rising at 3.8% as of September 2023, practically twice the two% acknowledged objective of the Fed.
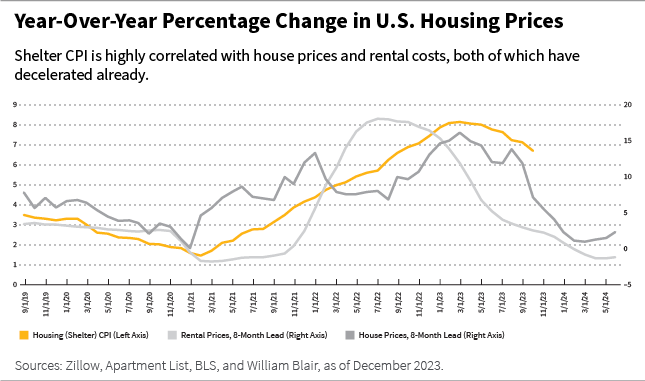
A better have a look at the elements of the value will increase means that the principal offender stays housing. It’s the single largest part of the CPI basket, weighing roughly one-third of the index.
The housing part of the CPI is an imprecise mix of housing costs and lease prices.
On-line platforms for dwelling buying and rents now make extra present pricing info available, and these worth tendencies recommend that the contribution of housing to the CPI is more likely to diminish considerably within the first half of 2024, as proven within the chart beneath.
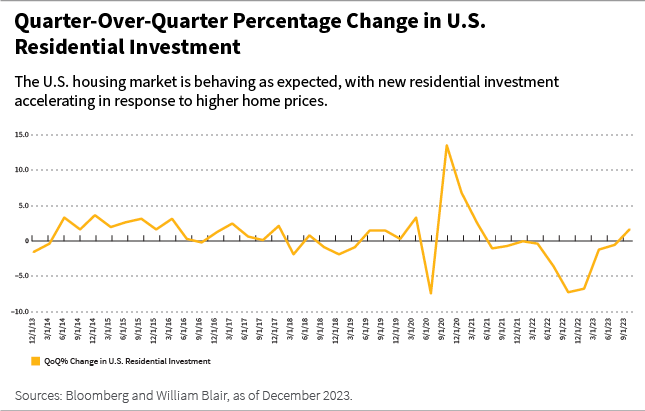
Latest home worth will increase have motivated extra constructing: residential funding has returned to progress after two years of steady declines, as proven within the chart beneath.
Over time, that is more likely to assist extra housing market exercise and mitigate future worth will increase.
Crucially, the labor market has healed because the post-pandemic provide constraints have all however unwound. Wage progress continues to reasonable; hourly earnings are actually rising at 4%, down from practically 6% a 12 months in the past.
The variety of job vacancies has continued to say no because the economic system has added 150,000 internet new jobs per 30 days for a lot of the second half of 2023.
In different phrases, the returning employees and resumption of immigrant inflows resolved the extreme employee provide scarcity with none significant decide up in unemployment.
Falling inflation is more likely to stay a strong tailwind to client spending and, by extension, general financial progress, as reasonable wage positive aspects in extra of falling inflation increase actual incomes.
This dynamic can also be taking part in out in Europe, the place the disinflation course of commenced later and has additional to run.
Financial progress is more likely to stay extra reasonable in Europe than in the US, not least attributable to important geopolitical tensions on its borders and meaningfully increased vitality costs in comparison with pre-pandemic ranges.
With items and providers costs already converging to pre-pandemic tendencies, it isn’t a stretch to imagine that U.S. inflation will normalize to its long-term 2% price within the first half of 2024.
Because the disinflation course of progresses, present financial coverage will de facto grow to be extra restrictive, suggesting that some moderation within the federal funds price will grow to be needed even when financial exercise stays resilient.
The ECB is simply as more likely to face low inflation and underwhelming progress in Europe inside months. Counting on at this time’s or, extra precisely, final month’s indicators of worth actions, dangers maintaining financial coverage too restrictive and punitive for future financial exercise.
We count on the Fed to deliver coverage charges all the way down to the three.5% vary on an 18-month view and to start this course of within the first half of 2024.
So, if the Fed adjusts its “impartial” financial coverage stance to be consistent with meaningfully decrease inflation and does so in a well timed method, and if the ECB follows swimsuit in Europe, the world’s principal demand facilities can preserve modest however sustainable financial progress in 2024.
In different phrases, 2024 would be the first 12 months of “regular” financial enlargement post-COVID.
[1] Bourses are represented by the DAX Index (Germany), the IBEX 35 Index (Spain), and the FTSE MIB Index (Italy).
[2] Japanese equities are represented by the Tokyo Value Index (TOPIX).
Editor’s Word: The abstract bullets for this text had been chosen by Searching for Alpha editors.




