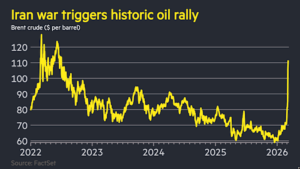
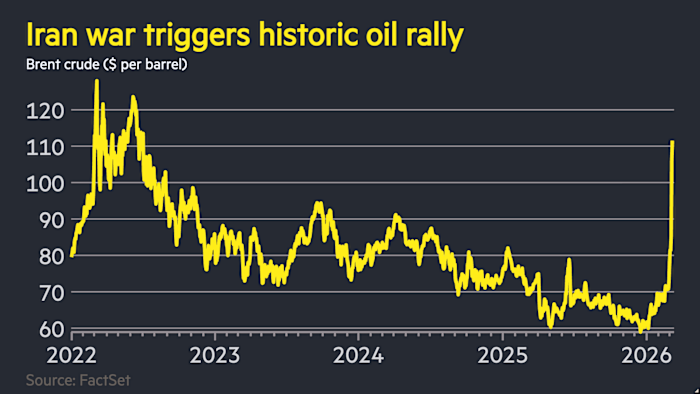
Baidu, a prominent Chinese tech company primarily known for its search engine, is set to enhance its main smartphone app by introducing direct access to the popular AI tool, OpenClaw. This feature will be available starting later today for users who opt in, allowing them to communicate with the AI agent to perform tasks such as scheduling, organizing files, and writing code. The surge in popularity of AI agents like OpenClaw is attributed to their capacity for automating various tasks, which include managing emails and interacting with online services.
Previously, OpenClaw was only available through messaging platforms such as WhatsApp and Telegram; however, Chinese tech giants including Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent have begun integrating it into their cloud systems. Baidu reports having 700 million monthly active users for its search app. In addition to enhancing the search app, the company plans to extend OpenClaw’s functionalities to its e-commerce platforms and other services.
This rollout coincides with the upcoming Lunar New Year holiday, a strategic move as Chinese internet companies strive to attract new users and capitalize on their AI investments. In a similar vein, Alibaba has integrated its e-commerce platform, Taobao, and the travel site Fliggy with its AI chatbot Qwen, which recently managed over 120 million consumer orders in just six days. Meanwhile, cybersecurity firms like CrowdStrike have raised concerns about the potential risks of giving OpenClaw unrestricted access to enterprise systems.
Why this story matters: The integration of AI tools into widely used applications reflects a significant trend in technological advancement and user convenience.
Key takeaway: Baidu’s launch of OpenClaw in its search app showcases the competitive landscape of AI adoption among major Chinese tech companies.
Opposing viewpoint: Experts caution against the excessive permissions granted to AI tools, citing potential cybersecurity threats and privacy concerns.